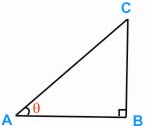
The sine of
an angle θ (sin θ as it is usually written) can be defined using
a right-angled triangle, in which θ is one of the angles as shown,
by
sin θ = BC = Length of side opposite to θ
AC length of hypotenuse.
For example, if a ladder of length 5 metres leans against a wall
at an angle of 65o
to the horizontal, the height h metres at which it touches the wall
is given by h/5 = sin 65o
so h = 5 sin 65o = 5 x 0.906 307 8
= 4.531 538 9
(to calculator accuracy)